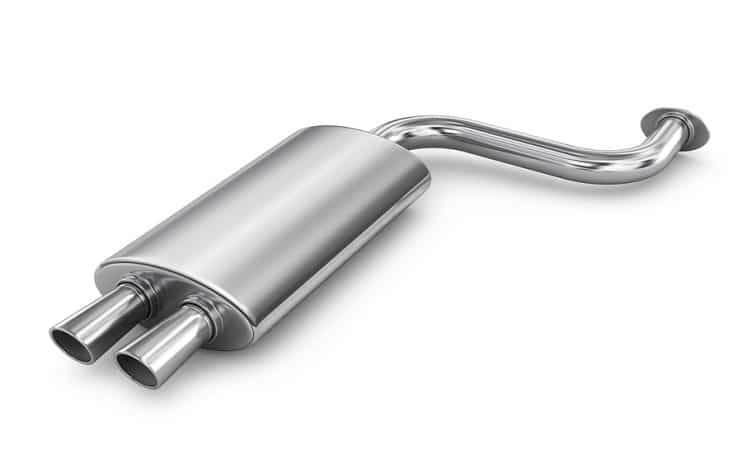

The exhaust back box, or rear silencer, is a key part of your car’s exhaust system. It reduces engine noise, manages exhaust gases, and ensures harmful fumes are safely directed away, all while helping your vehicle meet emissions standards. However, corrosion, exhaust leaks and wear and tear can all damage the exhaust back box, resulting in symptoms that are a sure sign it needs replacing.
Table of contents:
- What is the exhaust back box, and why is it so important?
- What are the signs of a failing back box?
- What causes problems with exhaust back boxes?
- How long does an exhaust back box last?
What is the exhaust back box, and why is it so important?
The exhaust back box is a crucial component of your car’s exhaust system. It’s responsible for reducing engine noise and managing the flow of exhaust gases. As part of a larger system, including the exhaust manifold and exhaust downpipe, the back box makes sure that harmful gases are safely directed away from your vehicle while minimising sound pollution.
A faulty or poorly maintained back box can disrupt the entire exhaust system, so you may need to replace it with a new or used exhaust back box. If you know a thing or two about cars, you’ll be aware that catching issues early on can save you money and time further down the road.
What are the signs of a failing back box?
Your vehicle’s exhaust back box is crucial in reducing noise and managing emissions. Here’s how to spot if it might be failing.
Noise
A failing back box often results in increased or unusual noise. You may hear a louder exhaust note or a rattling sound, which could be a sign of internal damage or a loose component.
Listen for changes in sound when starting your car or accelerating. Inspect the back box for visible damage or holes if the sound suddenly changes. A loud, raspy noise often points to internal baffle failure.
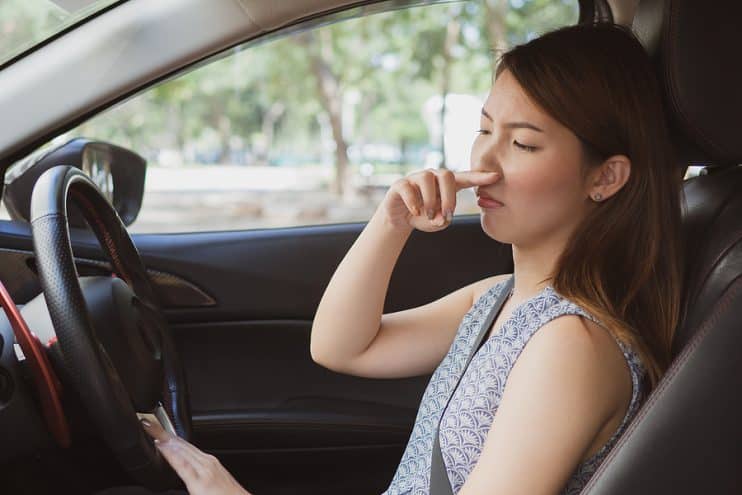

Harmful smells
If you notice a strong, unpleasant odour inside or around your car, exhaust fumes may be leaking. This could allow harmful gases like carbon monoxide to enter the cabin, posing a serious health risk.
If you do smell exhaust fumes, check the connections around the back box and exhaust pipes for leaks. Exhaust paste or clamps can temporarily fix minor issues, but a replacement might be necessary.
Decreased fuel efficiency and performance
A faulty back box can restrict the exhaust flow, causing the engine to work harder. This often results in reduced fuel efficiency and noticeable drops in performance, such as sluggish acceleration.
Monitor your fuel consumption regularly and inspect the back box and exhaust system for blockages or damage if you think you’re getting less mileage for your fuel. A clear exhaust path is crucial for engine efficiency.
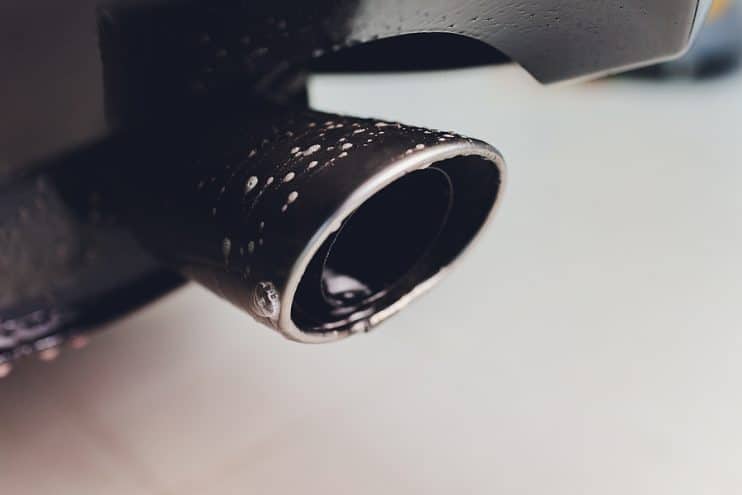
Rust, cracks, and corrosion
Check for visible rust or cracks on the back box. These signs of deterioration are common, especially in older vehicles or vehicles frequently exposed to wet or salted roads.
Inspect your back box after driving in winter conditions or through deep puddles. Rust can spread quickly, especially if the protective coating is damaged. Treating minor rust early with a rust converter can help, but severe corrosion means it’s time for a replacement.
Backfiring and misfires
A failing back box can disrupt the exhaust system’s balance, leading to backfiring or engine misfires. A noticeable popping sound often accompanies this.
Rattling or vibrations
Loose or broken parts inside the back box can cause noticeable rattling or vibrations, particularly during idling or acceleration.
Check under your car for any hanging or loose parts. Sometimes, the brackets holding the back box can corrode, causing it to hang loosely and rattle.

Moisture and condensation
Excessive moisture inside the exhaust system can lead to internal rusting. While some condensation is normal, large amounts of water dripping from the back box could indicate a problem.
After starting the engine, take a look at the exhaust pipe. A small amount of water is normal, but if it continuously drips, it may indicate that moisture is trapped inside, accelerating any rust.
What causes problems with exhaust back boxes?
Several factors can contribute to a failing exhaust back box:
- Corrosion: Constant exposure to moisture, road salt, and harsh weather accelerates rust and corrosion.
- Exhaust leaks: Cracks or loose connections allow exhaust gases to escape, reducing efficiency and safety.
- Poor installation: Incorrect fitting can cause misalignment, leading to stress on the exhaust system and premature failure.
- Wear and tear: Speed bumps, potholes, and road debris can damage the back box over time, especially if positioned low.
How long does an exhaust back box last?
An exhaust back box typically lasts between 3 to 7 years, depending on driving conditions and maintenance. Regular inspections are essential – check it at least once a year or during routine servicing. Addressing minor issues early can prevent costly repairs and keep your car running smoothly.
Whether you choose a new or used exhaust back box, keeping it in good condition ensures better performance and extends the life of your vehicle’s entire exhaust system.












.png)